最近部署在 Azure 上的 VM 经常因为某些原因被停用(Deallocated),遂想着写一个 PowerShell 脚本配置为 Windows 的计划任务来监控 Azure VM 的状态,一旦发现被停用了,自动启动 Azure VM。该脚本将用到 Azure PowerShell 提供的命令集,通过预先创建的 Azure service principal 来自动登录并获取 VM 状态,如果状态是 deallocated 就调用 Start-AzVm 命令来启动 VM,每次运行结果都会记录到本地日志。
安装 Azure PowerShell 命令集
Azure PowerShell 命令集可以运行在最新的 PowerShell 7.x 上或者 Windows 内置的 PowerShell 5.1 上。
PowerShell core 当前用户安装命令:
Install-Module -Name Az -AllowClobber -Scope CurrentUser
PowerShell core 所有用户安装命令:
Install-Module -Name Az -AllowClobber -Scope AllUsers
Windows 内置 PowerShell 5.1 安装命令:
Install-Module -Name PowerShellGet -Force
安装完成后可以执行 Connect-AzAccount,如果弹出了 Azure 登录窗口那么安装就成功了。
注意:如果想同时在 PowerShell 5.1 和 PowerShell 7.x 上使用 Azure PowerShell,那就得在这两个终端上都安装一次。
创建 Azure service principal
获取 VM 运行状态前需要先登录 Azure 账号。运行 Connect-AzAccount 可以交互式地登录 Azure,但是我们要创建的是自动化脚本,不可能采用这种交互式登录的方式,所以我们需要创建一个 Azure service principal 来代替我们人工登录。
首先运行
Connect-AzAccount登录到我们的 Azure 账号。登录后会自动选择到账号默认的 Tenant,通过
Get-AzVm -Name命令看看能否获取到我们想管理的 VM,如果成功获取到了那就直接下一步。如果没有获取到的话,则需要通过Set-AzContext -SubscriptionId来切换到 VM 所在 Subscription 所对应的 Tenant。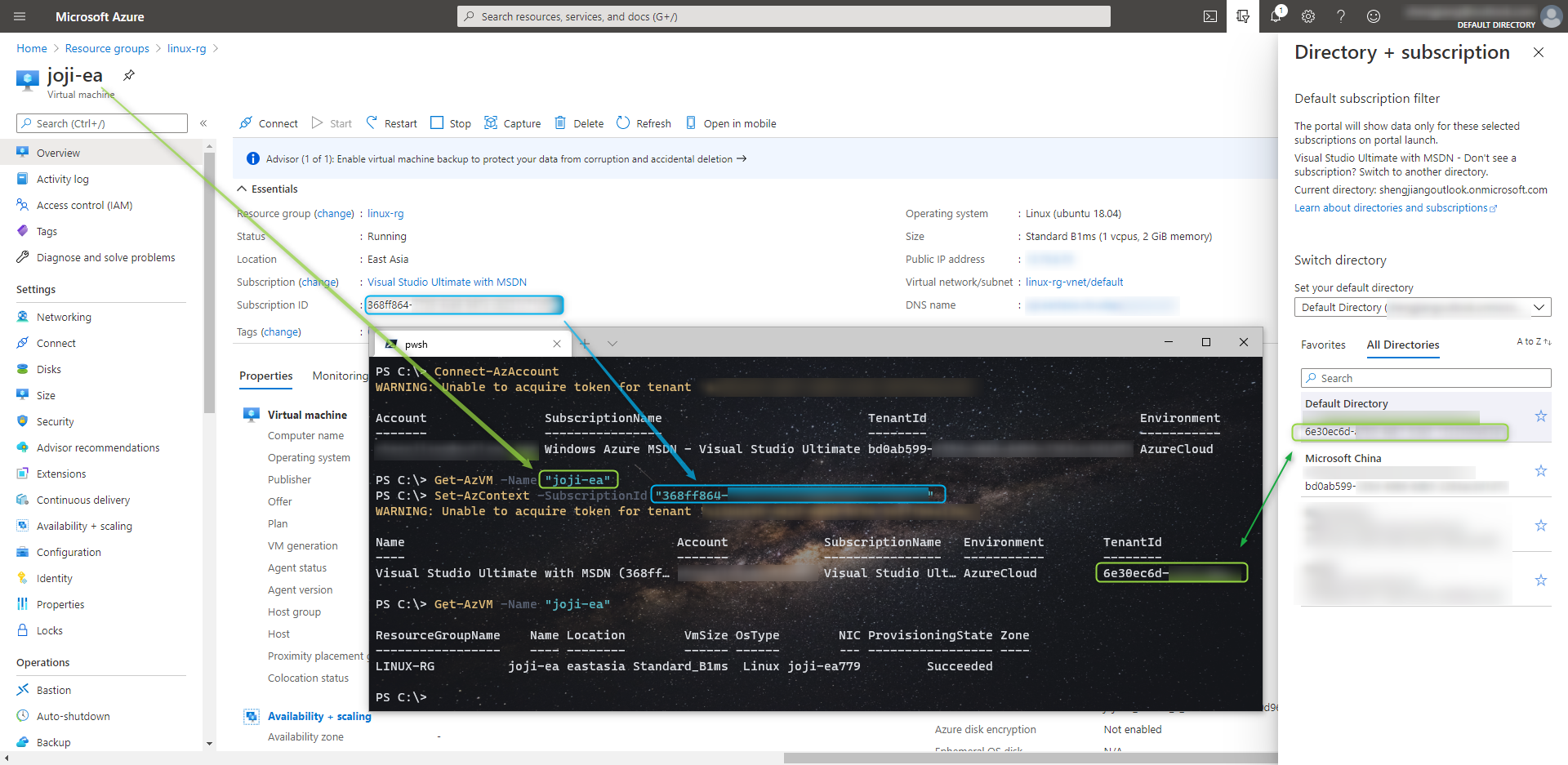
然后使用
New-AzADServicePrincipal创建一个 Azure service principal,指定一个 displayName 即可,会自动生成一个随机密码,通过以下方式可以把明文密码显示出来。$sp = New-AzADServicePrincipal -DisplayName "vm-powershell-script-svc-principal" $BSTR = [System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::SecureStringToBSTR($sp.Secret) $UnsecureSecret = [System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::PtrToStringAuto($BSTR) $UnsecureSecret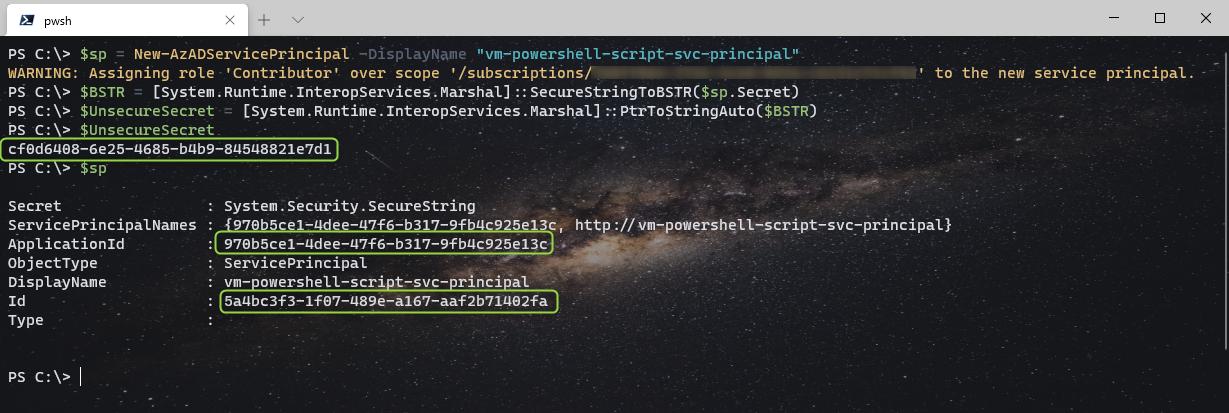
- ApplicationId 可以作为用户名登录 Azure
- UnsecureSecret 可以作为密码登录 Azure
- Id 可以作为
ObjectId传入Remove-AzADServicePrincipal -ObjectId来删除这个 Azure service principal
我们可以在
Disconnect-AzAccount后通过下面的命令验证是否可以成功使用刚才创建的 Azure service principal 登录并获取 VM 状态:$password = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "cf0d6408-6e25-4685-b4b9-84548821e7d1" -AsPlainText -Force $credential = New-Object -TypeName System.Management.Automation.PSCredential -ArgumentList "970b5ce1-4dee-47f6-b317-9fb4c925e13c", $password Connect-AzAccount -ServicePrincipal -Credential $credential -Tenant "6e30ec6d-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx" Get-AzVM -Name "joji-ea"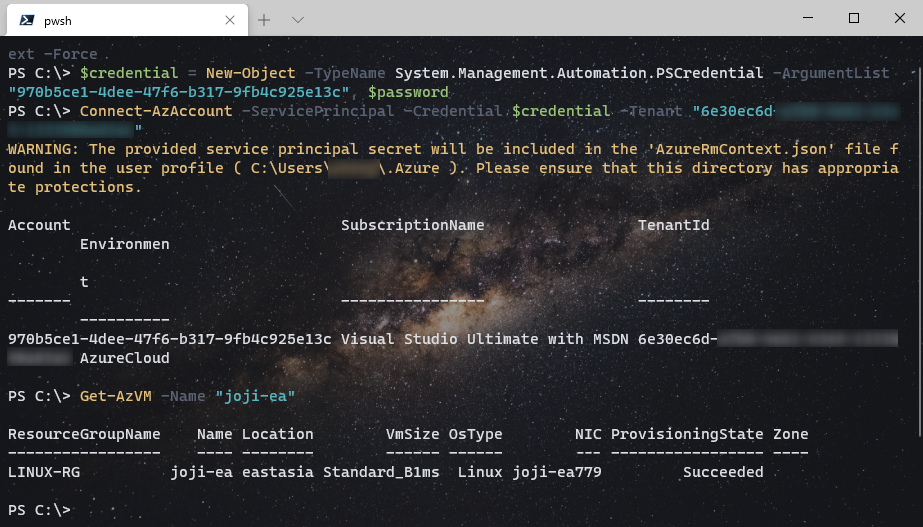
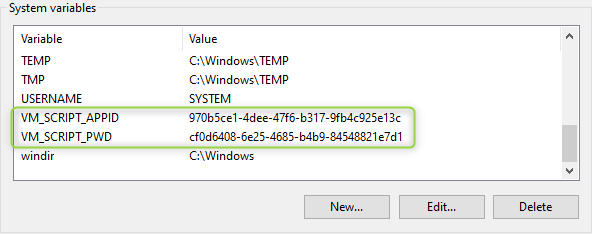
将用户名、密码配置为环境变量
把 Azure service princial 的用户名、密码直接写在脚本里不是很安全,我们选择把用户名、密码配置成为系统环境变量
脚本内容
其实只要登录这块跑通了,脚本本身逻辑还是很简单明了的,判断一下 VM 状态是否是 deallocated,是的话调用 Start-AzVm 来启动 VM,然后加上一个日志功能就算完工了。
function log($message) {
$global:logContent += "$(Get-Date -Format "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") $message`r`n"
}
$logFile = "c:\temp\vm.log"
$global:logContent = ""
if (!(Test-Path $logFile)) {
New-Item $logFile -Force
}
else {
$global:logContent = Get-Content $logFile -Raw
}
$password = ConvertTo-SecureString -String $Env:VM_SCRIPT_PWD -AsPlainText -Force
$credential = New-Object -TypeName System.Management.Automation.PSCredential -ArgumentList $Env:VM_SCRIPT_APPID, $password
Connect-AzAccount -ServicePrincipal -Credential $credential -Tenant "6e30ec6d-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx" -WarningAction SilentlyContinue
$vm = Get-AzVm -Name "joji-ea" -Status
log("VM PowerState: $($vm.PowerState)");
if ($vm.PowerState -match "deallocated") {
$startvm = Start-AzVm -Name "joji-ea" -ResourceGroupName "linux-rg"
log("Starting VM...`r`nOperationId: $($startvm.OperationId)`r`nStatus: $($startvm.Status)`r`nStartTime: $($startvm.StartTime.ToString())`r`nEndTime: $($startvm.EndTime.ToString())")
$newVMstatus = Get-AzVm -Name "joji-ea" -Status
log("Refreshing... VM PowerState: $($newVMstatus.PowerState)");
}
Set-Content $logFile $global:logContent.TrimEnd()
配置计划任务
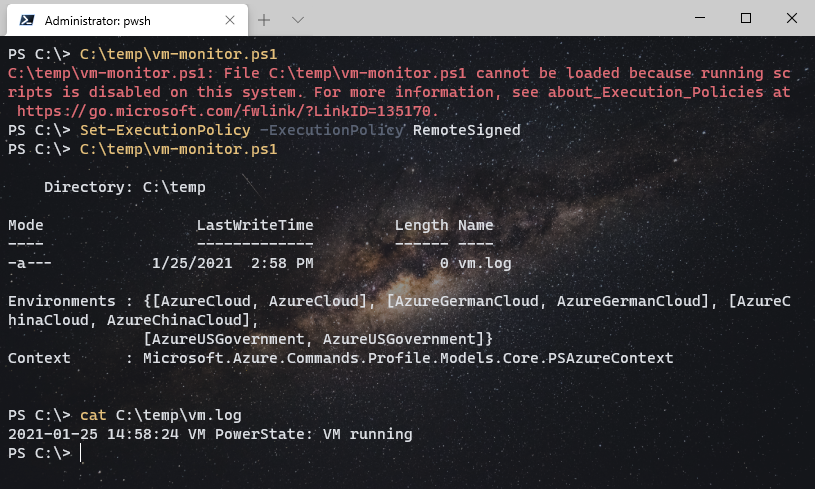
最后我们将配置一个计划任务来循环运行这个 PowerShell 脚本以达到监控效果。假设脚本保存在: "C:\temp\vm-monitor.ps1",先打开 PowerShell 运行 C:\temp\vm-monitor.ps1 确保脚本执行没有问题。Windows 上默认的 PowerShell 脚本 ExecutionPolicy是 Restricted,如果之前没有设置过 ExecutionPolicy,脚本是运行不了的,需要以管理员权限打开 PowerShell 并运行命令 Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned 来允许脚本运行。
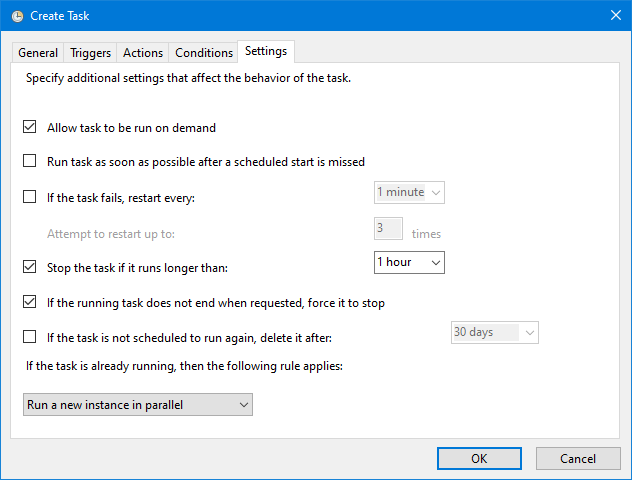
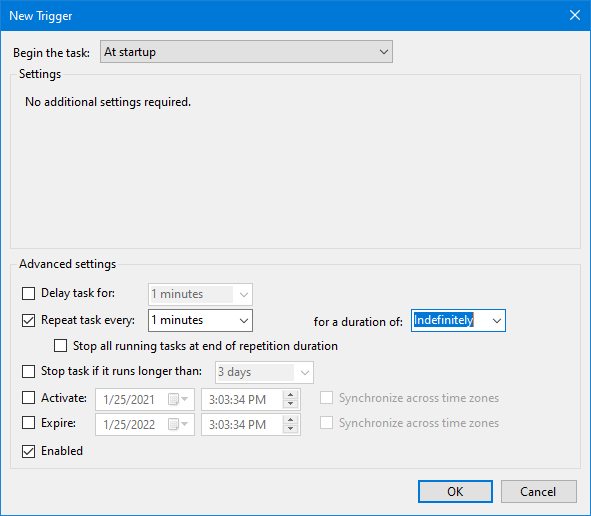
触发条件配置为:系统启动后就执行,之后每分钟执行一次。
任务执行命令为: pwsh -File c:\temp\vm-monitor.ps1,如果没有安装 PowerShell 7.x 的话,可以改为 powershell -File c:\temp\vm-monitor.ps1 使用 Windows 内置的 PowerShell。
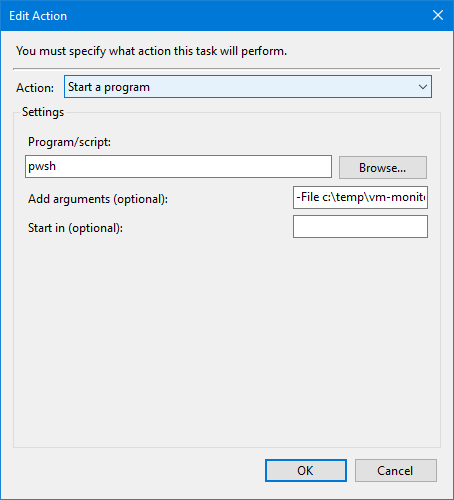
最后是一些其它的配置选项,比如:前一个任务还没运行完,那么起一个新的实例执行任务、如果任务执行超过 1 小时强制停止。